
Full text loading...
Nitrosomonas europaea is an aerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacterium that participates in the C and N cycles. N. europaea utilizes CO2 as its predominant carbon source, and is an obligate chemolithotroph, deriving all the reductant required for energy and biosynthesis from the oxidation of ammonia (NH3) to nitrite (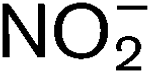 ). This bacterium fixes carbon via the Calvin–Benson–Bassham (CBB) cycle via a type I ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO). The RubisCO operon is composed of five genes, cbbLSQON. This gene organization is similar to that of the operon for ‘green-like’ type I RubisCOs in other organisms. The cbbR gene encoding the putative regulatory protein for RubisCO transcription was identified upstream of cbbL. This study showed that transcription of cbb genes was upregulated when the carbon source was limited, while amo, hao and other energy-harvesting-related genes were downregulated. N. europaea responds to carbon limitation by prioritizing resources towards key components for carbon assimilation. Unlike the situation for amo genes, NH3 was not required for the transcription of the cbb genes. All five cbb genes were only transcribed when an external energy source was provided. In actively growing cells, mRNAs from the five genes in the RubisCO operon were present at different levels, probably due to premature termination of transcription, rapid mRNA processing and mRNA degradation.
). This bacterium fixes carbon via the Calvin–Benson–Bassham (CBB) cycle via a type I ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO). The RubisCO operon is composed of five genes, cbbLSQON. This gene organization is similar to that of the operon for ‘green-like’ type I RubisCOs in other organisms. The cbbR gene encoding the putative regulatory protein for RubisCO transcription was identified upstream of cbbL. This study showed that transcription of cbb genes was upregulated when the carbon source was limited, while amo, hao and other energy-harvesting-related genes were downregulated. N. europaea responds to carbon limitation by prioritizing resources towards key components for carbon assimilation. Unlike the situation for amo genes, NH3 was not required for the transcription of the cbb genes. All five cbb genes were only transcribed when an external energy source was provided. In actively growing cells, mRNAs from the five genes in the RubisCO operon were present at different levels, probably due to premature termination of transcription, rapid mRNA processing and mRNA degradation.

Article metrics loading...

Full text loading...
References


Data & Media loading...
