
Full text loading...
The AmtB protein transports uncharged NH3 into the cell, but it also interacts with the nitrogen regulatory protein PII, which in turn regulates a variety of proteins involved in nitrogen fixation and utilization. Three PII homologues, GlnB, GlnK and GlnJ, have been identified in the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum, and they have roles in at least four overlapping and distinct functions, one of which is the post-translational regulation of nitrogenase activity. In R. rubrum, nitrogenase activity is tightly regulated in response to 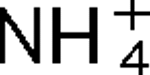 addition or energy depletion (shift to darkness), and this regulation is catalysed by the post-translational regulatory system encoded by draTG. Two amtB homologues, amtB
1 and amtB
2, have been identified in R. rubrum, and they are linked with glnJ and glnK, respectively. Mutants lacking AmtB1 are defective in their response to both
addition or energy depletion (shift to darkness), and this regulation is catalysed by the post-translational regulatory system encoded by draTG. Two amtB homologues, amtB
1 and amtB
2, have been identified in R. rubrum, and they are linked with glnJ and glnK, respectively. Mutants lacking AmtB1 are defective in their response to both  addition and darkness, while mutants lacking AmtB2 show little effect on the regulation of nitrogenase activity. These responses to darkness and
addition and darkness, while mutants lacking AmtB2 show little effect on the regulation of nitrogenase activity. These responses to darkness and 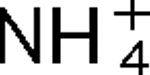 appear to involve different signal transduction pathways, and the poor response to darkness does not seem to be an indirect result of perturbation of internal pools of nitrogen. It is also shown that AmtB1 is necessary to sequester detectable amounts GlnJ to the cell membrane. These results suggest that some element of the AmtB1-PII regulatory system senses energy deprivation and a consistent model for the integration of nitrogen, carbon and energy signals by PII is proposed. Other results demonstrate a degree of specificity in interaction of AmtB1 with the different PII homologues in R. rubrum. Such interaction specificity might be important in explaining the way in which PII proteins regulate processes involved in nitrogen acquisition and utilization.
appear to involve different signal transduction pathways, and the poor response to darkness does not seem to be an indirect result of perturbation of internal pools of nitrogen. It is also shown that AmtB1 is necessary to sequester detectable amounts GlnJ to the cell membrane. These results suggest that some element of the AmtB1-PII regulatory system senses energy deprivation and a consistent model for the integration of nitrogen, carbon and energy signals by PII is proposed. Other results demonstrate a degree of specificity in interaction of AmtB1 with the different PII homologues in R. rubrum. Such interaction specificity might be important in explaining the way in which PII proteins regulate processes involved in nitrogen acquisition and utilization.

Article metrics loading...

Full text loading...
References


Data & Media loading...
