
Full text loading...
Differential extraction of Ca2+ from the cytoplasmic and vacuolar pools of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, using DEAE-dextran, revealed that most of the cellular Ca2+ was bound, precipitated or sequestered within the vacuole. When the concentration of Ca2+ in the medium was raised from 10–6
m to 10–3
m, cytoplasmic Ca2+ homeostasis was maintained at 5·8 × 10–6 to 2·3 × 10–5
m, whereas the vacuoles accumulated higher concentrations of Ca2+. The results indicate that the vacuoles function as a cytoplasmic Ca2+ buffering system and as the major sequestering organelle for Ca2+. A respiratory-deficient mutant (ρ°) displayed a similar intracellular distribution of Ca2+ to the wild-type. When cells were permeabilized by DEAE-dextran the vacuoles were still capable of Ca2+ uptake. This uptake proceeded without the addition of ATP or glucose in fresh preparations but required the addition of ATP after incubation of the permeabilized cells in buffered sorbitol for 2 h. The results are consistent with the proposed Ca2+/H+ antiport in the vacuolar membrane, which is driven by 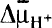 formed by the H+-ATPase pumping H+ into the vacuole.
formed by the H+-ATPase pumping H+ into the vacuole.

Article metrics loading...

Full text loading...
References


Data & Media loading...
